Folate and folic acid are forms of vitamin B9 used for deficiency and to prevent pregnancy complications. Many foods contain folate or have folic acid added.
Since 1998, folic acid has been added to cold cereals, flour, breads, pasta, bakery items, cookies, and crackers, as required by federal law. Foods that are naturally high in folate include leafy vegetables, okra, asparagus, certain fruits, beans, yeast, mushrooms, animal liver and kidney, orange juice, and tomato juice. Folic acid is also available as a supplement, and is often used in combination with other B vitamins.
Folic acid is used for preventing and treating low blood levels of folate (folate deficiency) and high blood levels of homocysteine (hyperhomocysteinemia). People who are pregnant or might become pregnant take folic acid to prevent serious birth defects such as spina bifida. Folic acid is also used for many other conditions including depression, stroke, decline in memory and thinking skills, and many others.
Uses & Effectiveness
Effective for
- Folate deficiency. Taking folic acid improves folate deficiency.
Likely Effective for
- High levels of homocysteine in the blood (hyperhomocysteinemia). This condition has been linked to heart disease and stroke. Taking folic acid by mouth lowers homocysteine levels in people with normal or high homocysteine levels and in people with kidney failure.
- Toxicity caused by the drug methotrexate. Taking folic acid by mouth seems to reduce nausea and vomiting from methotrexate treatment.
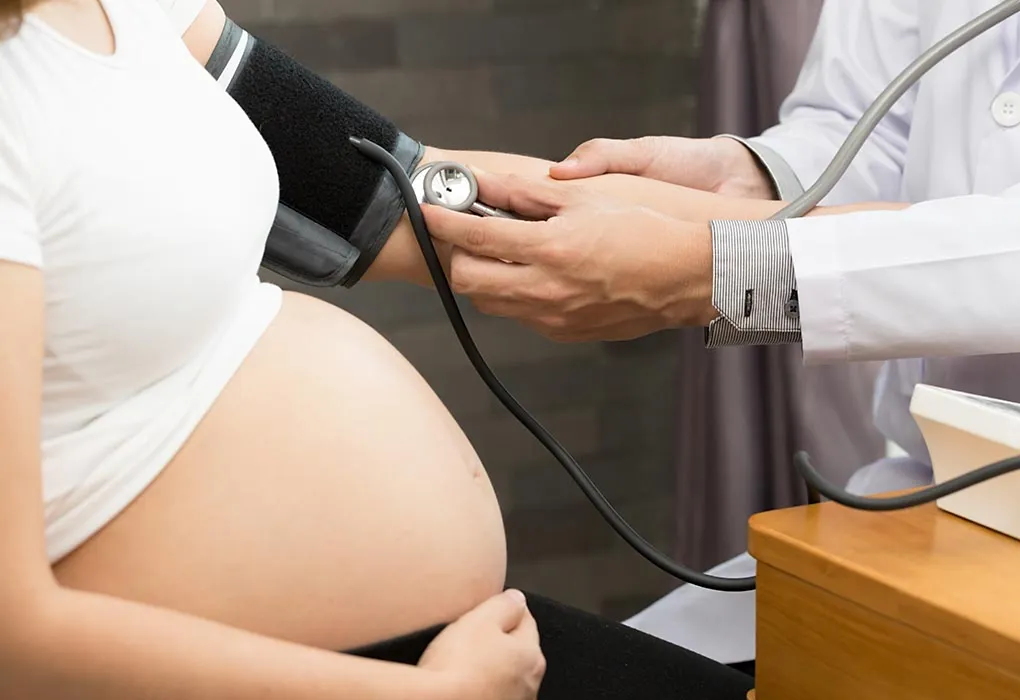
- Birth defects of the brain and spine (neural tube birth defects). Consuming folic acid 600-800 mcg by mouth daily during pregnancy reduces the risk of these birth defects. Folic acid can come from the diet or supplements. Some people who are at high risk should get 4000-5000 mcg daily.
Possibly Effective for
- Decline in memory and thinking skills in older people. Taking folic acid by mouth, with or without other supplements, may improve memory and thinking skills in older people who have a larger decline in thinking skills than expected at that age. But it doesn't seem to work in older people who are experiencing the usual decline in thinking skills for their age.
- Depression. Taking folic acid by mouth along with antidepressants seems to improve symptoms in some people with depression.
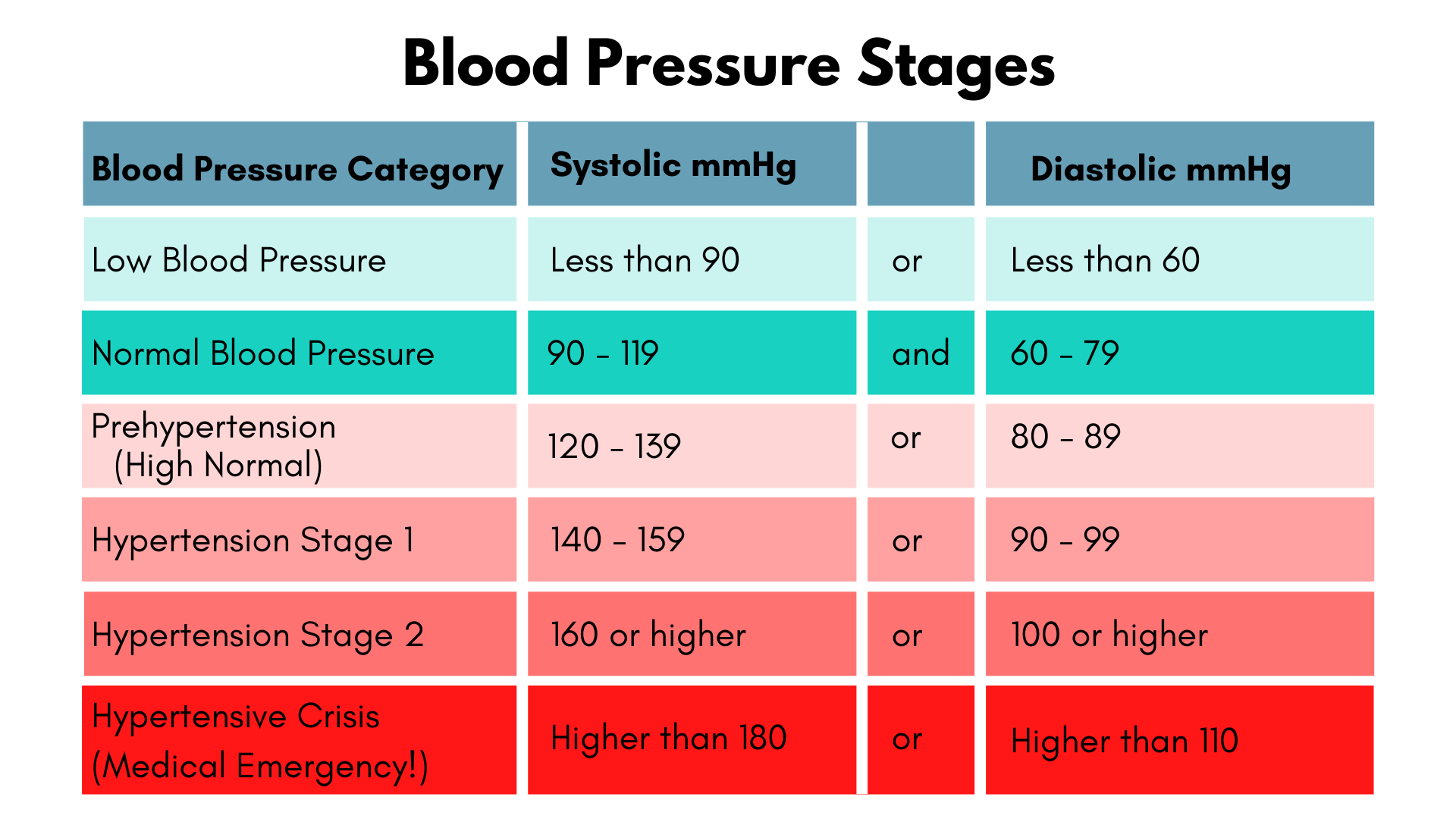
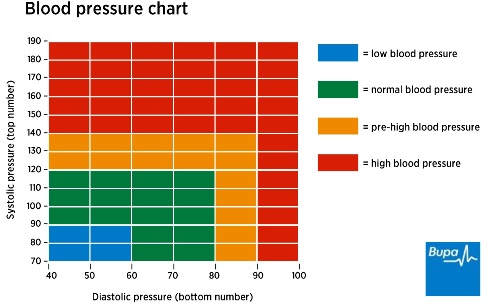
- High blood pressure. Taking folic acid by mouth daily for at least 6 weeks reduces blood pressure in some people with high blood pressure who are not taking other blood pressure medications.
- Gum enlargement caused by the drug phenytoin. Applying folic acid to the gums seems to prevent this issue. But taking folic acid by mouth doesn't seem to help.
- Stroke. In areas of the world that don't add folic acid to grain products, taking folic acid supplements can reduce the risk of stroke. But supplements don't seem to be helpful for people who live in countries that do add folic acid to grain products.
- A skin disorder that causes white patches to develop on the skin (vitiligo). Taking folic acid by mouth seems to improve symptoms of this condition.
Possibly Ineffective for
- Low levels of healthy red blood cells (anemia) due to iron deficiency. Adding folic acid to an iron supplement does not help to treat anemia any better than taking an iron supplement alone.
- Decline in memory and thinking skills that occurs normally with age. Taking folic acid by mouth doesn't seem to prevent a decline in mental function that occurs normally in healthy aging adults.
- Cataracts. Taking folic acid by mouth with vitamin B6 and vitamin B12 does not prevent cataracts. In fact, it might increase the number of cataracts that need to be removed.
- Diarrhea. Taking folic acid by mouth doesn't seem to prevent diarrhea in children who are at risk of malnutrition. In fact, it may even increase the risk of having diarrhea that lasts more than a few days.
- Fall prevention. Taking folic acid by mouth with vitamin B12 does not seem to prevent falls in older people who are also taking vitamin D.
- Male infertility. Taking folic acid by mouth, alone or with other ingredients, does not seem to improve male fertility.
- Death of an unborn or premature baby. Taking folic acid by mouth during pregnancy does not seem to reduce the risk of a baby dying just before or after birth. But it does help prevent other health issues in the baby.
- Cancer of the white blood cells (leukemia). Taking folate by mouth during pregnancy does not reduce the risk of this type of cancer in children.
- Weak and brittle bones (osteoporosis). In elderly individuals with osteoporosis, taking folic acid by mouth with vitamin B12 and/or vitamin B6 does not seem to prevent broken bones.
- Physical performance in elderly adults. Taking folic acid by mouth with vitamin B12 doesn't seem to help older people walk better or have stronger hands.
- High blood pressure during pregnancy. High-dose folic acid supplements do not seem to reduce blood pressure during pregnancy, or the risk of developing a condition called pre-eclampsia.
- Infection of the airways. Taking folic acid by mouth doesn't seem to prevent infections in the lungs in children at risk of malnutrition.
Reference:
- webmd.com/vitamins/ai/ingredientmono-1017/folic-acid











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cortisol-371314fd2ef34947969e615ee1e75691.jpg)











:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1281646803-2213a37421224e01848904cea84b587f.jpg)




 وبلاگ تخصصی سلامت شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است و اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با بهداشت، ایمنی، سلامتی بدن و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریها را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.
وبلاگ تخصصی سلامت شامل مجموعه مطالب پزشکی است و اطلاعات مفیدی در رابطه با بهداشت، ایمنی، سلامتی بدن و راه های پیشگیری از بیماریها را در اختیار شما کاربر محترم می گزارد.